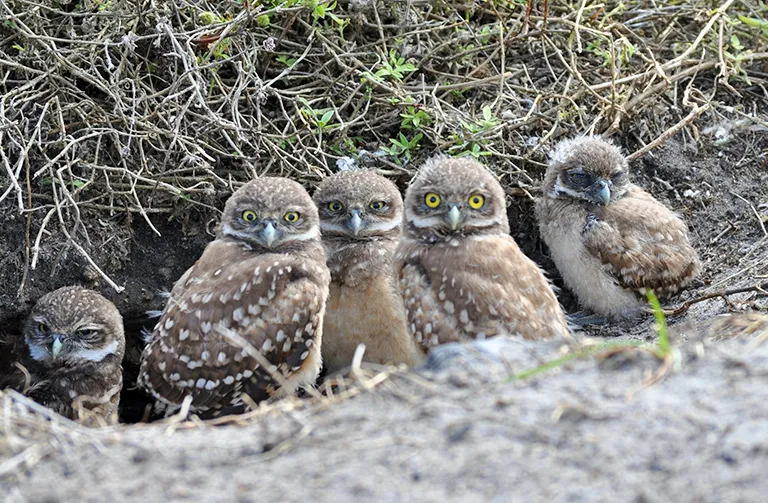
Burrowing Owl
At 100 square miles, Cape Coral, Florida is the second-largest city by land area in the state of Florida, with Jacksonville being the only larger city. Cape Coral also boasts the largest population of the Florida species of the Burrowing Owl (Athene cunicularia floridana) in the state, estimated at 1,000 nesting pairs.
Weighing only 5-8.5 ounces and standing 7.5-11 inches tall, the Burrowing Owl is one of the smallest owl species in the world, and it’s unique among the 171 owl species for living underground. Unlike the Western species of Burrowing Owl (Athene cunicularia hypugaea) that inhabits abandoned prairie dog burrows, Florida’s Burrowing Owls dig their own burrows. Cape Coral is home to more than 2,500 burrows within the city limits, though not all are actively used by owls.
Photographers and birders from around the world visit Cape Coral to see these charming owls, often amazed by how easily they can be observed and photographed. However, this accessibility comes at a price. Over the years, one of the main locations to observe Burrowing Owls has been the Cape Coral Library. Many burrows used to surround the library, all bustling with owl activity. Today, only one burrow remains active, possibly due to excessive human disturbance, causing the owls to seek quieter locations.
While some Western Burrowing Owls migrate, those in Cape Coral remain year-round but may seek shelter in the summer to avoid the intense heat. The best time to see these owls is from January through June, and if you want to catch a glimpse of their chicks, the best time is late April through June.

Rules of Engagement if You Visit Our Owls
- Download a map of suggested sites to search for owls on your own.
- Call Rotary Park Environment Center to sign up for a guided bus tour to see the Burrowing Owls and other wildlife of Cape Coral.
- Maintain a safe distance from the Burrowing Owls. Every known burrow in the city, located away from residential properties, has been marked with PVC pipes. Keep in mind that Burrowing Owl burrows can extend up to 10 feet, so the owl's living area may be outside the marked zone. It is not recommended to approach an owl closer than 20 feet or linger for extended periods. While owls may appear unperturbed by your presence, it disrupts their daily activities and may hinder their hunting for food, especially when chicks are present.
- Unlike other owl species, these owls are active during the day. They can often be observed sitting in front of their burrows or on nearby perches at any time. During nesting season, which lasts from February through July, the male stands guard over the burrow for hours, while the female tends to the eggs or young chicks. When the chicks are approximately 10 days old, they will start emerging from the burrow, and you'll see more of the female outside.
- For photographers, the best lighting conditions are during the first or last light of the day, as the harsh Florida sun is less favorable for great photos. For birders, mid-day, when the sun is at its hottest, is the least ideal time to observe the owls.
- Please do not feed the owls. Their diet consists of mice, roaches, small snakes, anoles, and frogs. Not crackers, peanuts, granola bars, or McDonald’s french fries!
Burrowing Owls in the News
23rd Annual Burrowing Owl Festival Recap
The 23rd Annual Burrowing Owl Festival & Wildlife and Environmental Expo was an unforgettable celebration of Cape Coral’s iconic burrowing owls and the natural beauty of Southwest Florida! Held on Saturday, February 22, 2025, the event brought together wildlife...
Social media influencer donates land for burrowing owls
In a heartfelt act of conservation, Alexandra Fasulo, a former Cape Coral resident and advocate for wildlife preservation, has donated her 10,000-square-foot lot to the Cape Coral Wildlife Trust (CCWT).
Former Resident’s Land Donation Provides Sanctuary for Cape Coral’s Threatened Burrowing Owls Amid Rapid Development
In a heartfelt act of conservation, Alexandra Fasulo, a former Cape Coral resident and advocate for wildlife preservation, has donated her 10,000-square-foot lot to the Cape Coral Wildlife Trust (CCWT).
How to Help Burrowing Owls Displaced After Hurricanes
Published by Wink News by Amy GaloHurricanes Helene and Milton left many burrowing owls homeless, and Pascha Donaldson, a board member of the Cape Coral Wildlife Trust, is working hard to get them back into their burrows. Donaldson straps on her pink gloves, marches...
Cape Coral Construction Displaces Burrowing Owls, Sparks Community Outrage
A Cape Coral resident is raising concerns after witnessing the destruction of a burrowing owl habitat.
Early Thursday morning, around 8:30 a.m., concerned neighbor Amanda Goodwin says she saw the bulldozing of the protective sign for burrowing owls at the construction site at NE 8th Place and NE 11th Street.
Goodwin says she saw a white pickup truck with a tractor dismantling the sign. NBC2 even spotted a displaced owl while at the construction site.
Nick Jennings from FWC to Discuss Burrowing Owls
Did you know that Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission (FWC) biologists have an active program to band Cape Coral’s burrowing owls? Join Cape Coral Friends of Wildlife (CCFW) at their first general meeting of the season on September 10, 2024 to learn more...